- The video tutorial contains a high-level overview of the profiling tools available for Cuda workloads
- shows an example of how to use the tools to identify a cude performance issue

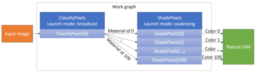
- The article presents a new D3D12 work graph sample to demonstrate how to classify screen space materials
- presents a high-level overview of the demo application
- additionally presents how the Radeon GPU Profiler can visualize the performance of work graph applications
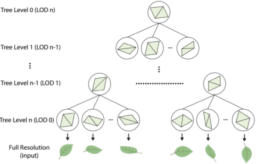
- The article explains the Tencent tree rendering system
- explains how tree information is compressed, automatic LODs are generated, as well as how GPU-driven rendering techniques are used for efficient rendering
- provides videos to show the LOD transitions as well as comparison against (older versions of) Nanite
- the article presents a robust solution to resolve self-intersection issues with secondary rays
- the proposed solution works by calculating error bounds and offset the starting point to lie outside of these bounds
- presents methods to reduce floating point numerical issues through using the suitable coordinate space and operation ordering
- HLSL and GLSL implementations are provided
Do you want the chance to work with clients like Google, Microsoft, Activision, Qualcomm and other AAA studios?
This is an opportunity to join a world-leader in advanced real-time graphics who are working at the cutting-edge of the game industry.
- Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science or equivalent
- Experience with DirectX 12, Vulkan, Metal, or other current rendering API
- 2+ years professional graphics programming experience
Please apply with your resume attached by replying to jiayi.zhuo@theforge.dev

- the blog post provides best practices for shader performance
- covers generic shader advice, as well as vertex/pixel/tesselation/compute specific advice

- the video presents a deep dive into the technical aspects of Starfield
- covering ship geometry details, materials, lighting, cities, landscapes, character details as well as reflections
- additionally, look at the loading structure, loading times, and brief frame-rate discussion

- the article presents how to use geometry shaders from OpenGL
- provides an overview of what geometry shaders are and how they can be used to overcome some vertex shader limitations
- implements a simple shader that calculates normals for a displaced plane first
- expands the implementation for billboarding, explaining the math and the implementation

Thanks to Cort Stratton for support of this series.
Would you like to see your name here too? Become a Patreon of this series.