- how the stylized vfx in Rime was implemented
- short overview of fire and smoke effect
- in-depth overview of the water rendering implementation

- explanation how to query reflection information from SPIR-V shader
- brief overview of the the SPIR-V type system
- explanation of the implementation of Pixel Projected Reflections using vulkan
- supports approximation of normal maps and roughness
- comparison against brute force ray tracing implementation (image quality and performance)

- how to implement a ray tracer using a compute shader in unity
- features supported: sky box, ground plane, spheres, reflections, directional light with hard shadows and a basic material system
- simple temporal anti-aliasing solution

- shows the steps leading up the final implementation
- uses a fixed weight for all contributing samples. If sample doesn’t contribute, blend in the current average color instead
- clamping sample size when sample is further away then the center sample. This makes sure out of focus background do not blur into in-focus foreground objects
- texture compression library in just 500 lines of C code + Zstd
- zpng compressing is quicker, takes 6% of the time and output size of the image is 66% compared to the png reference
- presentations from the Vulkan Montreal dev day
- including updates about HLSL in Vulkan and descriptor indexing

- comparison of Draco and mesh optimizer output in regards to size and decoding time
- Draco size compression is mesh dependent, can be larger. Always a lot slower to decode
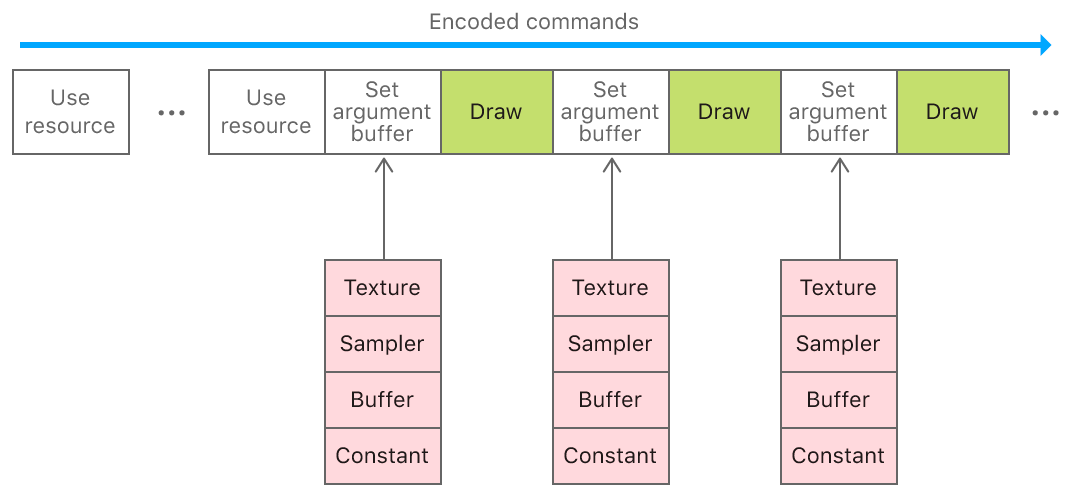
- examples for arguments buffer have been published
- allow the grouping of resources and constants into a single object that can be bound as a single unit
- tool that allows simplifications for static VR environments
- takes RGB + depth as input images
- generates simplified geometry that textures will be mapped onto to represent the scene
- prebuild version can be found here: https://github.com/ddiakopoulos/seurat/releases

- build upon the ideas of moment shadow mapping
transparent geometry is rendered twice
- determine transmittance function per pixel
- composite all transparent surfaces
taking advantage of the fact that the logarithm of the transmittance can be accumulated additively

- overview of the new rendering API
- build around method chaining for the initialization of descriptors

