- the blog post discusses changes in the latest release of Pix
- adds support for VRS shading rate visualization, shader graph debugging, as well as improved custom shader support
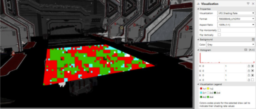
- the article provides a detailed discussion of how hardware implements the UNORM/SNORM conversion rules
- explaining special cases and how to deal with those
- additionally, it presents a C++ implementation of the presented concepts
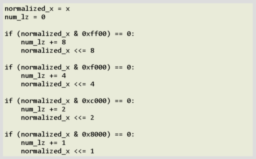
- the paper presents a model of applying motion blur to spheres in a 2.5D setting
- implemented by pre-generating an atlas of blurred spheres of varying radius and lighting angles and compositing these into the scene
- explains the implementation and limitations
- runnable example and source code is provided
- the blog post discusses changes done to the Disney Hyperion render since the prequel to the movie
- provides published research papers on the discussed techniques
- then presents the main challenges of the Moana 2 production and how they solved them

- the blog post discusses the difference between adjugate transpose vs inverse transpose of normals
- explains how it behaves on shading normals
- presents the visual results of different methods

- the video provides an introduction into the mathematics of importance sampling
- discusses how samples can approximate integrals
- then applies the ideas to the diffuse shading integral

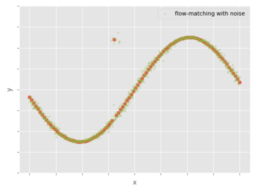
- the article explains and shows how noise applied to a curve fitting application changes the results
- additionally presents the same in a multi-modality model using flow matching
- concluding that “noise cancels out, signal adds up” cannot always be relied upon anymore
- the blog post presents tools available to visualize and understand memory usage in PyTorch
- explains how to estimate memory usage before running a workload
- additionally provides a small tool to help with the estimation
Thanks to Nia Bickford for support of this series.
Would you like to see your name here too? Become a Patreon of this series.