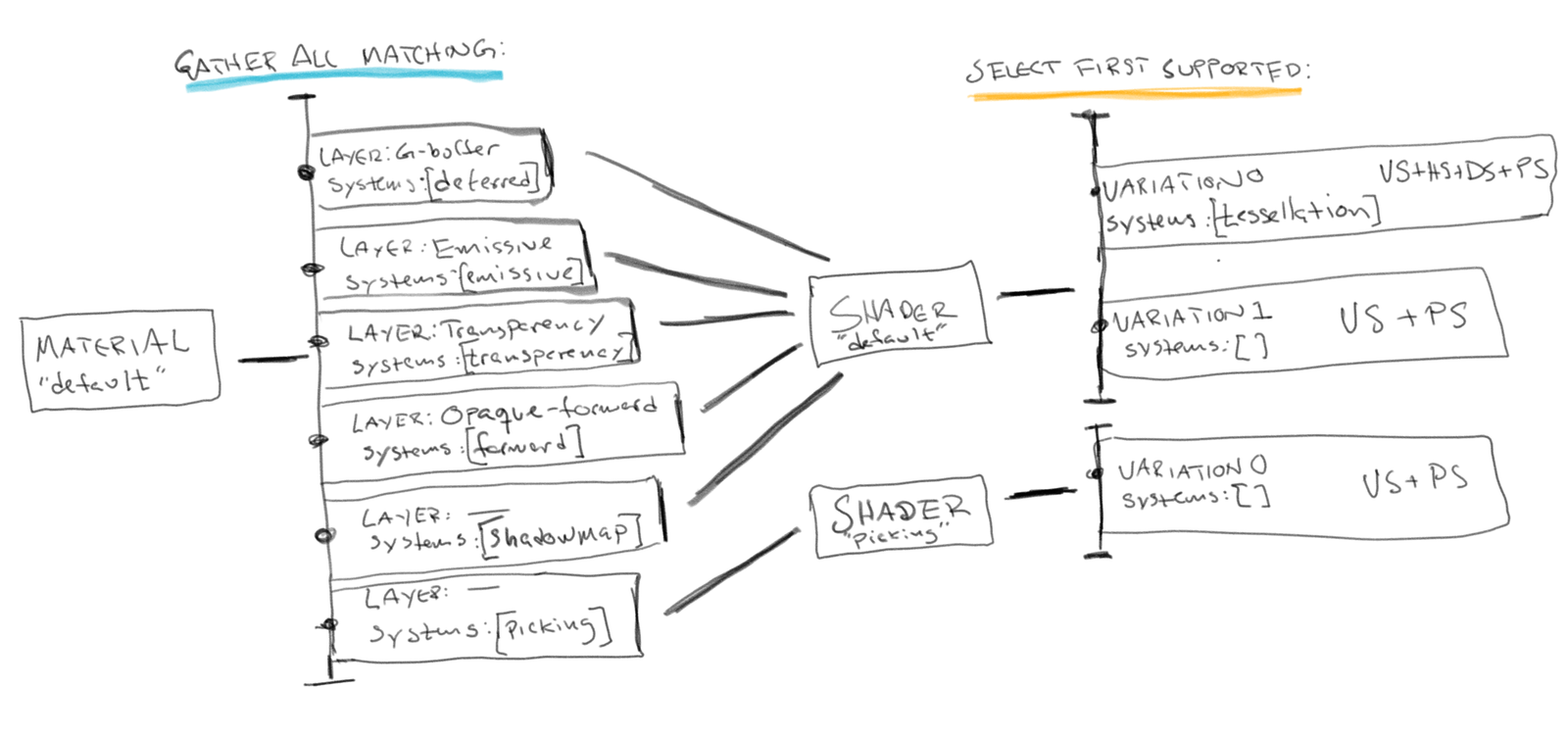
- shader authors can define variations of shaders with a number of systems
- each system can inject code/resources/constants into the shader
- a material allows specifications of which shaders belong together, which systems they use and allows to insert command at the correct time in the Frame
- all of the resulting shaders get a shared resource binder and constant buffer to reduce
explanations how ray tracing shaders in OpenGL can access the necessary textures for all objects in the world using GL_ARB_bindless_texture
- moving the scene information into group shared memory to speed up the ray tracing code a lot
- problems on metal, slower unless passing data by value instead of by const reference
- look at the iOS implementation with an overview of performance tools for CPU and GPU

- now using Logarithmic depth buffer when available
- writes custom depth in a pixel shader, this does disable early depth optimizations but still a performance win for their use-case
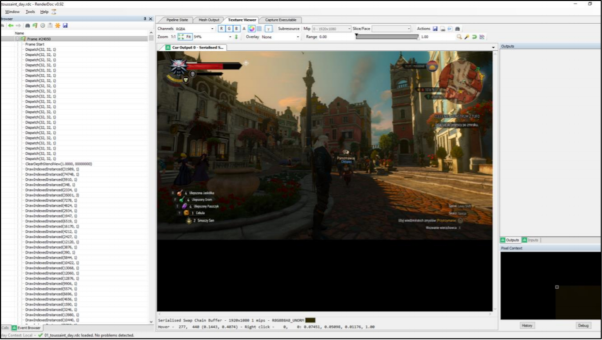
- look at the implementation of Witcher 3 rendering from an outside perspective using RenderDoc
- breakdown of rendering Frame structure
- how normals are stored in the g-buffer
- explanation of a number of techniques from the d3d disassembly
- sun rendering
- blinking stars
- eye adaptation
- tonemapping
- vignette
- discussion of tradeoffs for the basis file format
- comparison of different images formats transcoded from the same source format

- extending previous work in CNN(Convolutional neural network) based denoising
- using a modular architecture that improves temporal stability and detail preservation

- the longer the CPU/GPU can idle, the less power is needed
- optimizing a CPU bound game might cause more frames to be rendered (hitting 60 fps instead of 30). causing less GPU idle time and increasing power consumption
- kernel heuristics might trigger higher frequency mode which increases battery usage significantly
- Tutorial about the implementation of water surface movement of using a flow map in unity
- how to deal with deformation of normals using derivative maps
- NVIDIA Nsight Systems visualizes system-wide application interactions across CPU and GPU
- Nsight
- Volta, Vulkan 1.1 and Cuda 9.2, are supported
- user configurable memory view
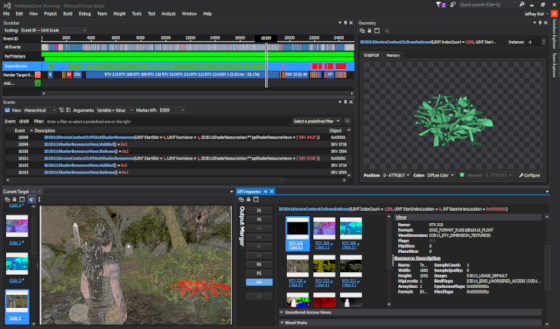
-how to investigate GPU starvation and detect CPU/GPU synchronizations and overview of other tools

