- comparison of combinations of six different sampling strategies for disk area light sources and 9 sample sequences
- testing is done for wholly and partially illuminated regions
- the best result could be achieved with the polar4 strategy introduced in this paper with well-stratified samples
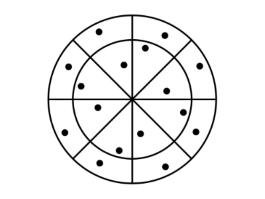
- introduction of new strategies to generate progressive(hierarchical) 2D sample point sequences
- can be stopped at any point in the sequence and samples will still be well distributed
- comparison against existing techniques, using many different distribution functions and shapes
- explanation and derivation of the HSV and HSL color spaces
- how to convert the color spaces to and from RGB colors
- implementation of a hybrid approach that mixes rasterization for first hit and raytracing for secondary rays
- tracing against polygons using compute shaders directly (no raytracing API)
- how to create a BVH structure and traverse it
- details about how to raytrace for shadows and reflections
- look at the performance, mainly memory bound
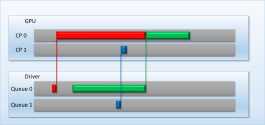
- provides an overview of GPU preemption strategies and how these affect application responsiveness and latency
- explains the physical properties of cameras, starting with a pinhole camera model
- shows the effect of changing focal length, aperture radius and how to implement this into a raytracer
- extending the concepts into a lens based camera system
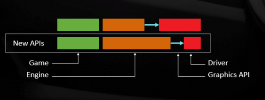
- explanation of performance culture, a working culture that treats performance as a core feature
- designed from the beginning and it’s everyone responsibility to uphold it
- video and slides from a talk that explains lessons learned from porting an AAA engine to Vulkan
- recommendations for memory, descriptors, command buffers and barrier management
- a short overview of frame graph architecture to achieve better barrier usage
- overview of the hybrid real-time rendering pipeline developed for PICA PICA demo
- layered material model
- transparency
- translucency
- shadows
- an in-depth look at the reflection system and global illumination system

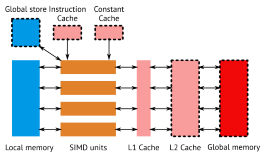
- how GPUs evolved from fixed function hardware to the uniform architecture used today
- overview of concepts required to understand the programming model
- how GPUs are able to hide memory latency to achieve higher throughput
summary of the paper “High-Performance Procedural Noise using a Histogram-Preserving Blending Operator” that was discussed in issue 45
- steps that the author recommends programmers follow that are interested in getting started in graphics programming
- from shadertoy (for instant visual feedback) to game engines to more low-level aspects of the implementation
- overview of the SDF storage system
- how the world space SDF is generated from a list of brushes and how it is modified at runtime
- how to raytrace against the distance field efficiently
- soft shadows and ambient occlusion improvements
- SDF → mesh conversion for moving particles

- overview of design decisions of single header low-level rendering API
- comparison against bgfx and sokol_gfx
- windows registry contains entries for Explicit Layers (all layers that can be loaded by a process) and Implicit Layers (all layers that will be loaded automatically for every process)
- sometimes these values will become corrupted