Daniel Jones has made a video summary of the articles included in this article available on Youtube
- the video presents an in-depth walkthrough that shows how to use signed distance fields (SDF) to create an animated girl
- explains all used primitives as SDW, how they are combined, and the lighting implementation
- implementation is done in shadertoy

- the article shows how The Witcher 3 implements a fullscreen effect that gives the world a painterly look
- presents a step-by-step walkthrough, showing all components that define the noise generation
- author provides a shadertoy implementation of the effect

- the post presents a bi-planar mapping as an alternative to tri-planar mapping using only two texture fetches
- starts by giving an overview of the tri-planar mapping
- followed by an explanation of the bi-planar mapping technique, presenting strategies to improve the quality and how the quality compares

- a very detailed article about depth buffers
- focusing on Unity, but most of the information is engine agnostic
- explains the different spaces, storage formats, and precision considerations
- additionally shows how to calculate world space positions from the depth buffer

- A Unity video tutorial that explains how to generate grass meshes using Compute shaders
- covers the setup, mesh generation, and LOD selection

- the article shows how Multiple Importance Sampling in 1D is used to improve the convergence of stochastic algorithms
- presents multiple experiments and shows how different techniques can reduce the sampling error
- a collection of resources (books, talks, websites) the author recommends for beginners to get started with graphics programming

- the presentation provides an overview of Variable Rate Shading (VRS), the different features levels
- provides insights into VRS performance, features that disable VRS, and what bottlenecks will cause VRS to not offer performance improvements
- additionally shows how to integrate the AMD helper library to generate the VRS screenspace map

- the presentation explains the ray tracing denoising technique developed by AMD
- shows what inputs are used, how the algorithm uses these to decide ray count, and how to use temporal reprojection to further reduce sample counts
- the code for the technique is provided, and the website includes comparison pictures and images of the intermediate results

- the post explains what changes have been made to the Vulkan raytracing extension since the preview specification
- extension has been split into 3 layers (acceleration structure, raytracing shaders states, and ray queries)
- walkthrough of each stage of the extensions
- in contrast to DXR, Vulkan offers the ability to generate acceleration structures on the CPU
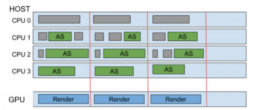
- the article presents an overview of how Vulkan raytracing has been implemented into Wolfenstein
- provides a brief overview of the different API concepts and how they are used

- the article contains an overview of the new features that will be included in shader model 6.6
- 64-bit Integer Atomic Operations, Dynamic Resource Binding, Compute Shader Derivatives and Samples, Packed 8-Bit Operations and variable Wave Size

Thanks to atyuwen for support of this series.
Would you like to see your name here too? Become a Patreon of this series.